Frequently Asked Questions
- Getting Started
- Backup Console
- Management Console
- Windows Backup
- Mac Backup
- Linux Backup
- Mobile Backup
- Cloud Applications Backup
- Server Cloud Backup
- Mass Deployment
- Entire Machine Backup
- Google Drive Backup
- IDrive® 360 Express
- Single Sign-On
- System Requirements
- Account Management
- Security
- Firewall Guidance
MS SQL Server
If your question is not addressed below, contact us through our support form and we will get back to you shortly.
- How do I perform a differential backup of my MS SQL Server using IDrive® 360?
- How can I perform incremental backup of my MS SQL server?
- How can I perform forced full backup of my MS SQL server?
- Under what name and extension are MS SQL Server backup files stored on IDrive® 360?
- Can I back up databases from multiple instances of MS SQL Server?
- I am unable to view the databases in the MS SQL Server instance that I am logged into. Why?
- Can I backup the MS SQL server in the 'Mirror Path' mode?
- Can I back up the Microsoft SQL Server 'tempdb' database?
- How do I restore my database backup file to my Microsoft SQL Server?
- Can IDrive® 360 back up the entire SQL Server database?
- Can I restore my database file to a different MS SQL Server database?
- When should I restore the MS SQL Server 'master' Database?
- How do I restore the MS SQL server master database?
- When should I restore the 'model', 'msdb', and 'distribution' databases?
- My MS SQL restore operation failed. How do I proceed?
- I am receiving the error "VDS::Create Fails: 0x80770005" during MS SQL Server backup. Why?
- I am receiving the error 'Check registration of SQLVDI.DLL and value of IID' during MS SQL Server backup. Why?
- Can I restore database files to multiple MS SQL Server instances?
- How do I assign the 'sysadmin' role to the "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" or "BUILTIN\Administrators group" in my MS SQL server?
- What recovery models does IDrive® 360 support for Microsoft SQL Server database backup and restore?
- Does IDrive® 360 support backup or restore of SQL databases with unicode characters in the database name?
- How do I run the MS SQL Server instance using an administrator or local account?
- How can I back up an MS SQL Server database to a NAS or mapped network drive?
- How can I restore an MS SQL Server database backup from a NAS or mapped network drive
- How do I change the database recovery model from Simple to Full or Bulk-logged to enable incremental backup?
- How do I remove the MS SQL server databases that are not required for restore?
How do I perform a differential backup of my MS SQL Server using IDrive® 360?
To perform differential backup,
- Sign in to the IDrive 360 desktop application and click 'Server Backup'. A slider menu will appear.
- Click 'MS SQL'. The MS SQL connection screen appears. By default, 'MS SQL backup' is selected.
- Provide the relevant authentication information when prompted. IDrive 360 provides two modes of MS SQL server authentication. Click 'Connect to MS SQL'.
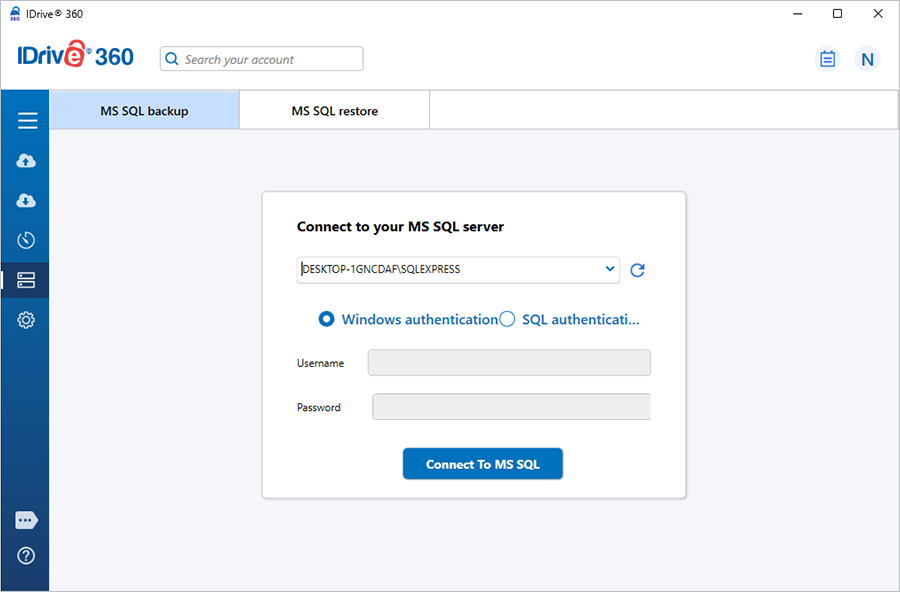
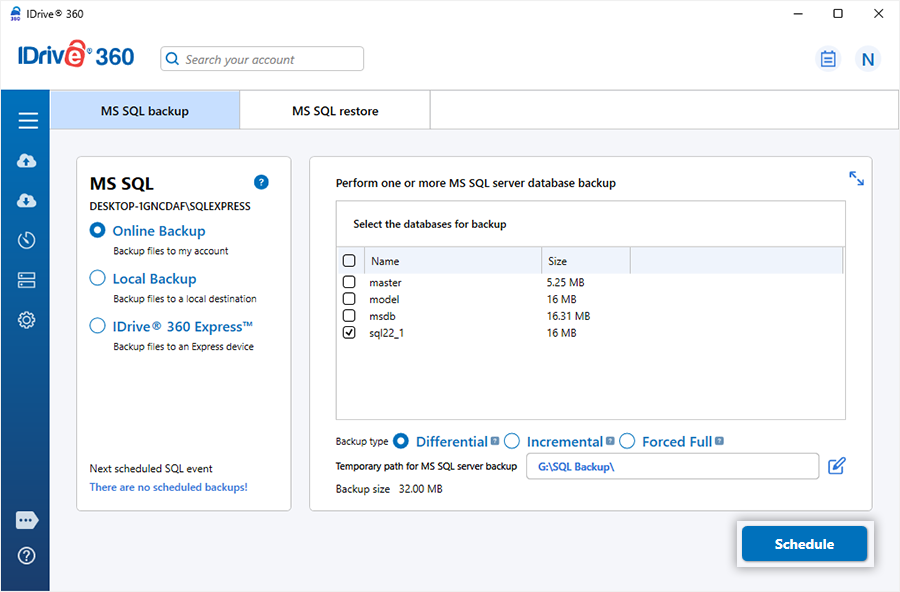
- Select 'Online Backup', 'Local Backup', or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup'.
On selecting 'Online Backup', the data will be stored on the IDrive® 360 cloud. On selecting 'Local Backup' or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup', the data will be stored in the local drive. - Select the databases from the list and specify MS SQL backup temporary path for local backup.
- Select backup type as 'Differential'.
- Click 'Schedule'.
The 'Scheduler’ appears, from where you can schedule the backup for any future day and time or perform an immediate backup of the selected databases.
- Click 'Save Changes'.
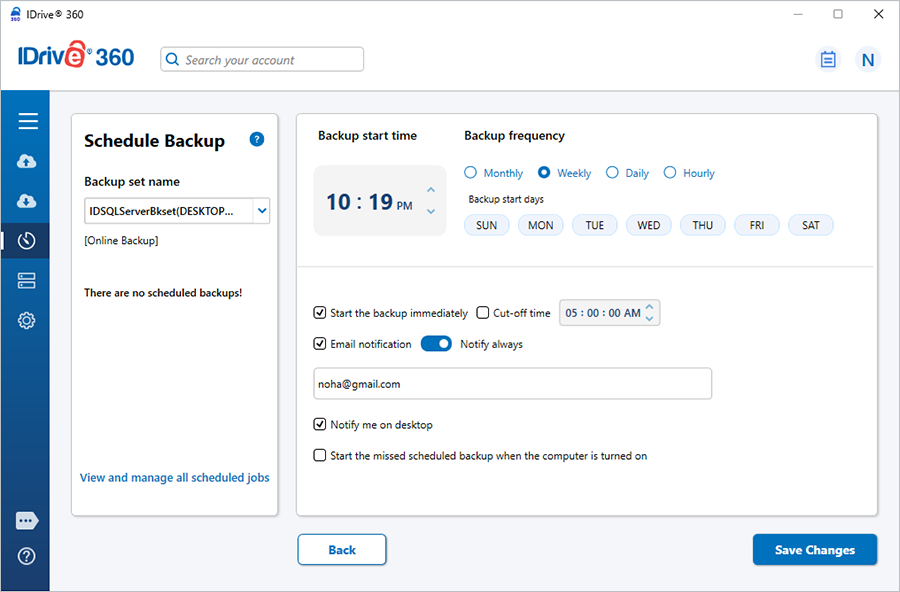
Note: Once the local backup is initiated, '.ServerBackup' folder is auto-created.
-
Note: IDrive 360 for Windows allows you to schedule the MS SQL server backup for different instances. For easy identification of the SQL server backup set, the name of the backup set will be 'IDSQLServerBkset' followed by the instance name scheduled for backup.
Example: If the instance name is 'MJOHN\INSTMJOHN', then the backup job name will be 'IDSQLServerBkset (MJOHN##INSTMJOHN)'.
How can I perform incremental backup of my MS SQL server?
To perform incremental backup,
- Sign in to the IDrive® 360 desktop application and click 'Server Backup'. A slider menu will appear.
- Click 'MS SQL'. The MS SQL connection screen appears. By default, 'MS SQL backup' is selected.

- Provide the relevant authentication information when prompted. IDrive® 360 provides two modes of MS SQL Server authentication. Click 'Connect to MS SQL'.

- Select 'Online Backup', 'Local Backup', or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup'.
On selecting 'Online Backup', the data is stored on the IDrive® 360 cloud. On selecting 'Local Backup' or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup', the data is stored on the local drive.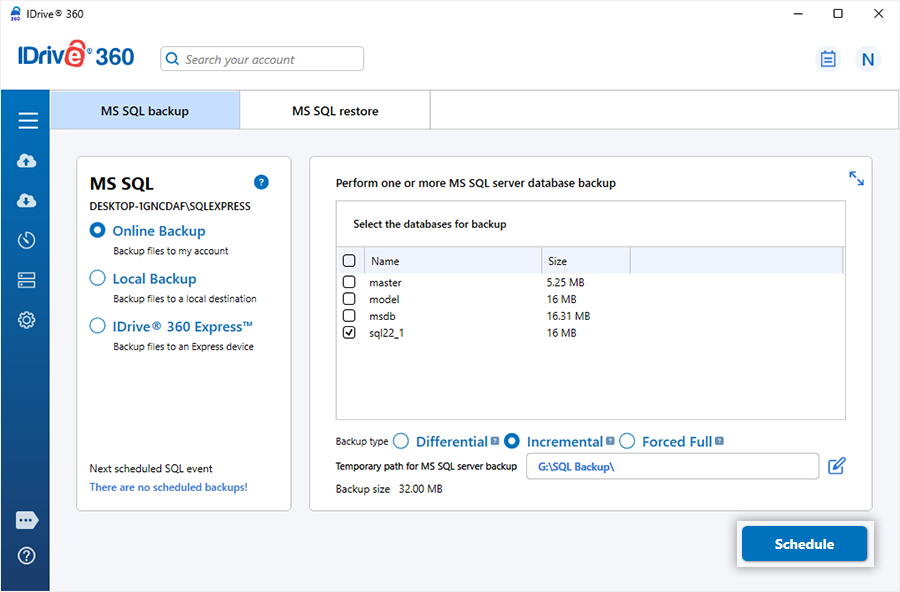
- Select the databases from the list and select the 'Incremental' option.
- Select backup type as 'Incremental'.
- Specify the local backup location and click 'Schedule'.
- In the 'Scheduler’, schedule the backup for any future date and time or perform an immediate backup. Click 'Save Changes'.

Note: To perform the incremental backup, the database should be in full/bulk-logged recovery model.
How can I perform forced full backup of my MS SQL server?
The Forceful Full backup option performs a complete backup of your MS SQL Server every time, regardless of previous backup states, ensuring full data protection.
To perform forced full backup,
- Sign in to the IDrive® 360 desktop application and click 'Server Backup'. A slider menu will appear.
- Click 'MS SQL'. The MS SQL connection screen appears. By default, 'MS SQL backup' is selected.

- Provide the required authentication details. IDrive® 360 provides two MS SQL server authentication modes. Click 'Connect to MS SQL'.

- Select 'Online Backup', 'Local Backup', or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup'.
On selecting 'Online Backup', the data will be stored on the IDrive® 360 cloud whereas on selecting 'Local Backup' or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup' the data will be stored in the local drive.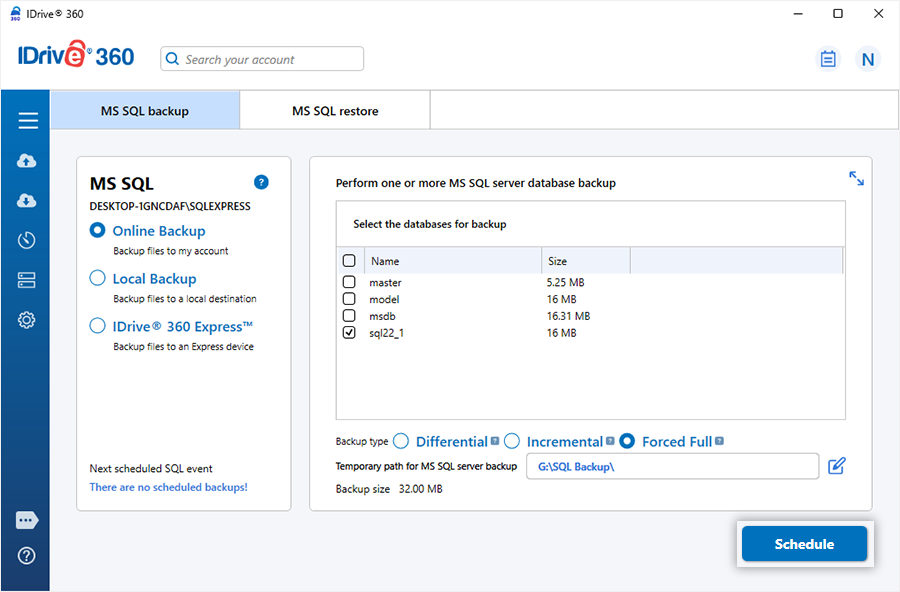
- Select the databases from the list and choose 'Forced Full' as the backup type.
- Specify the local backup location and click 'Schedule'.
- In the 'Scheduler’, schedule the backup for any future date and time or perform an immediate backup.
- Click 'Save Changes'.

Under what name and extension are MS SQL Server backup files stored on IDrive® 360?
MS SQL Server backup files are stored in your IDrive 360 account with the ‘.dmp’ extension. The file names are enclosed in square brackets.
File name format: [<database_name>].dmp
Examples: [model].dmp, [pubs].dmp, [order list].dmp.
Can I back up databases from multiple instances of MS SQL Server?
Yes. You can back up databases from multiple MS SQL Server instances running on the same local computer. However, backing up databases from MS SQL Server instances located on different machines across the network may not be supported.
I am unable to view the databases in the MS SQL Server instance that I am logged into. Why?
This issue may occur if the logged-in user account does not have sufficient permissions to view all databases in the instance. Contact your database administrator to obtain the required access privileges.
Can I back up the MS SQL server in 'Mirror Path' mode?
No. Even if you choose the Mirror Path option, the backups are still created using the Relative Path.
Can I back up the Microsoft SQL Server 'tempdb' database?
No. The ‘tempdb’ database cannot be backed up because it is a temporary system database that is recreated each time the SQL Server service restarts.
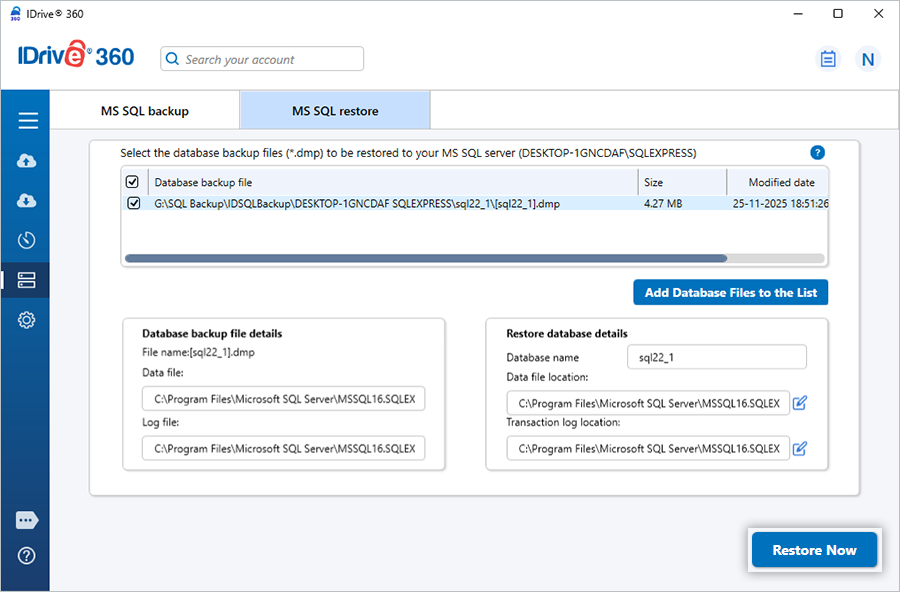
How do I restore my database backup file to my Microsoft SQL Server?
IDrive 360 lets you restore your database backup file to a different database and perform point-in-time recovery.
To restore your MS SQL database backup,
- Sign in to the IDrive® 360 desktop application and click 'Restore'.
- Select 'Online Restore', 'Local Restore', or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Restore'.
- If you select ‘Local Restore’, choose the required file version from the ‘Version’ list. - Locate and select the database backup file (IDSQLBackup) in your IDrive 360 account or local drive.
- Click 'Restore Now' to restore the IDSQLBackup file to your local computer.
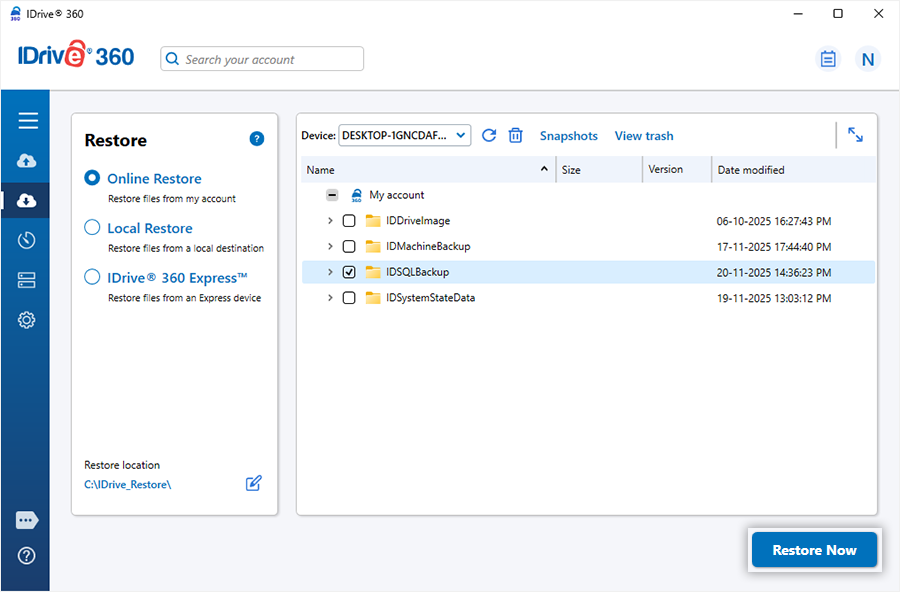
- Once the file is restored, click 'Server Backup'. The slider menu appears.
- Click 'MS SQL'. The MS SQL connection screen appears.

- Click 'MS SQL restore'.
- Provide the required Microsoft SQL Server authentication details when prompted.
- Click 'Connect to MS SQL'.
- Browse and select the restored IDSQLBackup file.
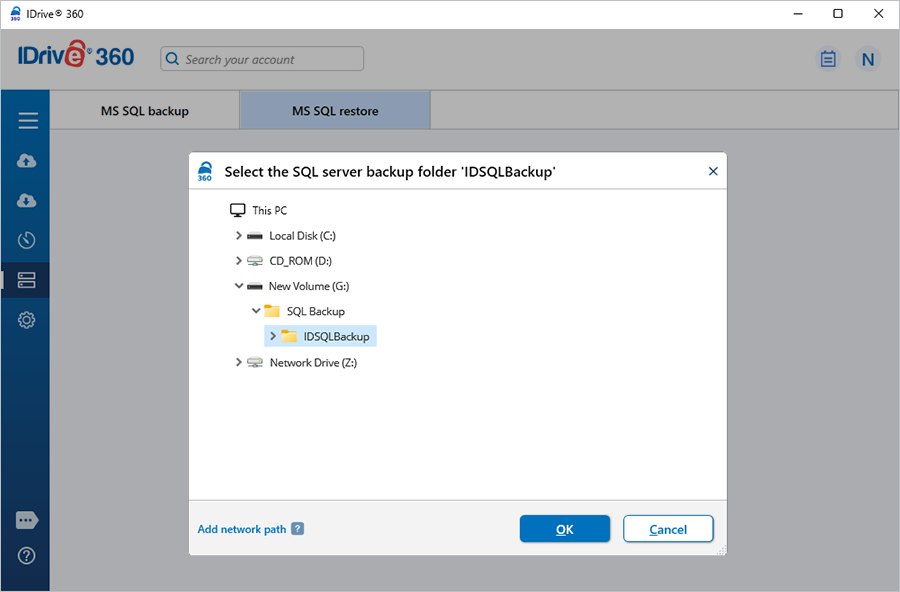
- Click 'Restore Now' to restore the database backup to your SQL Server.
Can IDrive® 360 back up the entire SQL Server database?
Yes. IDrive 360 can back up the entire MS SQL Server database along with the associated transaction log file, preserving the complete database structure and components in your online account.
You can also back up multiple databases. Each database is backed up as a separate dump file in the format [<database_name>].dmp.
Can I restore my database file to a different MS SQL Server database?
Yes. You can restore your database backup file (.dmp) to a different database by specifying a new database name during the restore process. You can also modify the data file and transaction log file locations as required.

When should I restore the MS SQL Server 'master' Database?
You should restore the master database in the following situations:
- When the master database is corrupted, or SQL Server cannot start due to system database failure.
- When you need to recover system-level metadata such as login accounts, server configuration settings, linked server definitions, or database file locations.
- After rebuilding the master database or reinstalling the SQL Server instance and needing to restore system-level information.
- When recovering from a failed configuration change that prevents SQL Server from functioning properly.
Note: Restoring the master database is not necessary if you are restoring only a user database.
For more information about the Microsoft SQL Server master database, visit http://www.microsoft.com/sql/.
How do I restore the MS SQL server master database?
To restore the master database,
- Start SQL Server in 'Single User Mode'.
- In the Start menu, click 'Run'.
- Type 'compmgmt.msc' and click 'OK' to open ‘Computer Management’.
- Go to 'Services and Applications' > 'SQL Server Configuration Manager'.
- Click 'SQL Server Services'.
- Right-click the SQL Server ('Instance') service and select 'Properties'.
- Click 'Startup Parameters'.
- Add the parameter -m and click 'OK'.
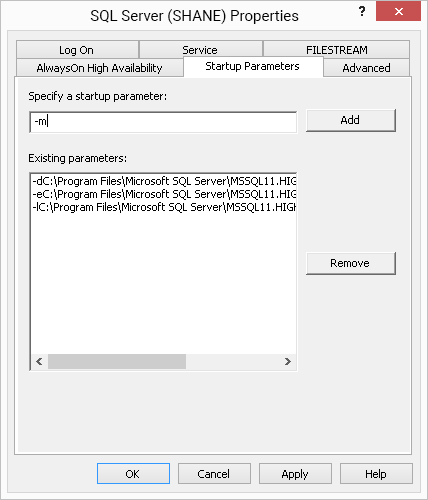
- Restart 'SQL Server Service'.
- Open the IDrive® 360 desktop application.
- Use the ‘MS SQL restore’ option to restore the master database backup.
Ensure IDrive 360 Service runs with Administrator privileges:
- In the Start menu, click ‘Run’, type services.msc, and press Enter.
- Right-click 'IDriveService' and go to 'Properties' > Log on > 'This Account'.
- Enter the Administrator credentials.
- Restart IDrive 360 service.
- In SQL Server, assign the 'sysadmin' role to the Administrator account.
When should I restore the 'model', 'msdb', and 'distribution' databases?
You should restore these SQL Server system databases under the following conditions:
model
Restore the model database if the database template has been modified or corrupted, affecting the creation of new databases.
msdb
Restore the msdb database when you need to recover SQL Server Agent jobs, backup and restore history, schedules, alerts, or maintenance plans.
distribution
Restore the distribution database if replication is configured and you need to recover replication settings, configuration data, or distribution history.
These system databases do not need to be restored when restoring a user database.
For more information about the model, msdb, and distribution databases, visit http://www.microsoft.com/sql/.
My MS SQL restore operation failed. How do I proceed?
If the restore operation fails with the following Microsoft ODBC error:
‘Use the WITH REPLACE or WITH STOPAT clause of the RESTORE statement. Restore Database is terminating abnormally.’
This error typically occurs when a database with the same name already exists or when restoring over an existing database without proper options.
To resolve this issue:
- Use the ‘WITH REPLACE’ or ‘WITH STOPAT’ clause in the RESTORE statement.
- We recommend modifying the database name, data file location, and transaction log file location before performing the restore again.
This prevents conflicts with existing databases and allows the restore to complete successfully.
I am receiving the error "VDS::Create Fails: 0x80770005" during MS SQL Server backup. Why?
This error indicates that the SQL Server service is running under a startup account using the format .\UserName, which may not have sufficient privileges to access required system resources.
How to resolve:
- Ask your system administrator to change the SQL Server service startup account to LocalSystem, or
- Use a startup account with the full domain format instead of the dot prefix.
For example: ‘DomainName\UserName’ instead of ‘.\UserName’
Ensuring the service runs under an account with appropriate permissions will allow the backup to proceed successfully.
I am receiving the error 'Check registration of SQLVDI.DLL and value of IID' during MS SQL Server backup. Why?
This error occurs when the application attempts to use the SQLVDI.DLL file, but the file is not registered correctly in the system.
To resolve this issue,
- Stop the SQL Server service.
- Click Start > Run, type Regsvr32 \SQLVDI.DLL, and click 'OK'.
The default location of the SQLVDI.DLL file is 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\80\COM.' - Restart the SQL Server service.
Re-registering the SQLVDI.DLL file ensures proper communication between SQL Server and the backup application.
Can I restore database files to multiple MS SQL Server instances?
Yes. You can restore database backup files to multiple SQL Server instances, but each restore must be performed separately, one instance at a time.
How do I assign the 'sysadmin' role to the "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" or "BUILTIN\Administrators group" in my MS SQL server?
In SQL Server 2008 and earlier, the 'sysadmin' role is automatically granted to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM and BUILTIN\Administrators.
For SQL Server 2012 and later, you must manually assign the 'sysadmin' role to these accounts or groups.
You can assign the sysadmin role using either SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or SQL command-line tools.
- SQL Server Management Studio::
- Open 'SQL Server Management Studio'.
- In ‘Object Explorer’, go to 'Security' > 'Logins' > 'NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM'.
- Right-click 'NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM' and select 'Properties'.
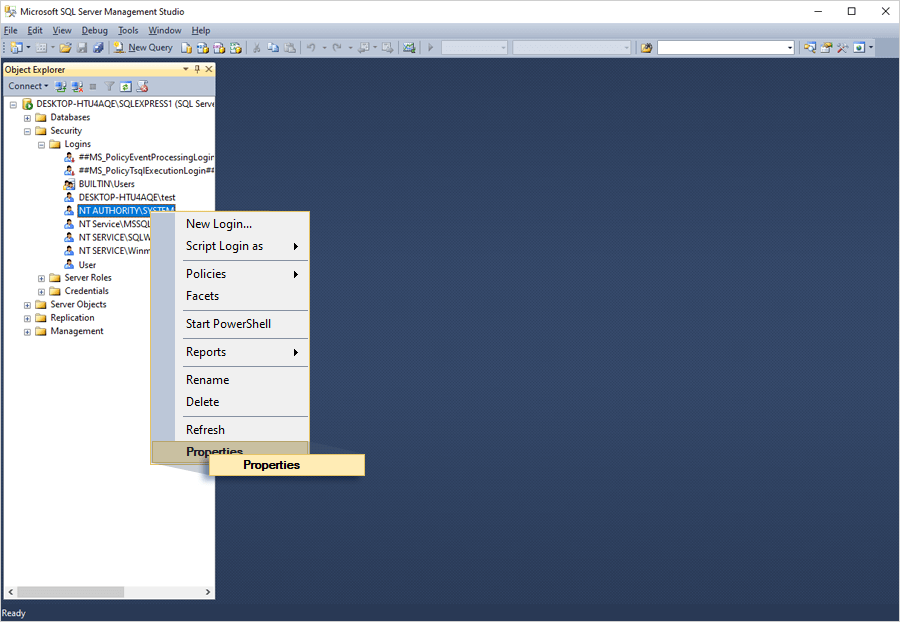
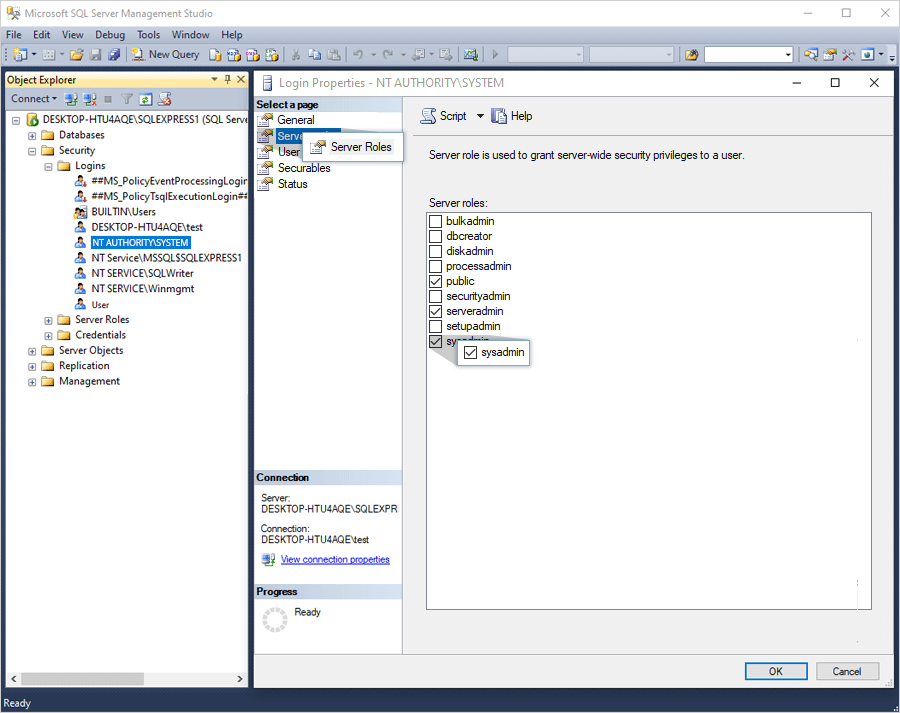
- In the 'Login Properties- NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM' window, click 'Server Roles'.
- Select the 'sysadmin' checkbox, and click 'OK'.
- SQL Server Command Line:
- Open Command Prompt with administrator privileges.
- Connect to SQL Server using Windows Authentication:
sqlcmd -S <ComputerName>\<InstanceName> Or (for default instance) sqlcmd -S <ComputerName>
- Run the following command to assign the sysadmin role:
exec sp_addsrvrolemember 'NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM', 'sysadmin' ;
go;
What recovery models does IDrive® 360 support for Microsoft SQL Server database backup and restore?
A recovery model is a database property that determines how transactions are logged, whether the transaction log can be backed up, and which restore operations are supported.
IDrive® 360 supports database backup, restore, and recovery operations based on the following Microsoft SQL Server recovery models:
- Simple Recovery Model
- Supports full and differential backups
- Does not support transaction log (incremental) backups.
- Full Recovery Model
- Records all transactions in the transaction log.
- Supports full, differential, and transaction log (incremental) backups.
- Allows point-in-time recovery.
- Transaction log backups include all changes since the last log backup.
- Bulk-Logged Recovery Model
- Similar to the Full Recovery Model but minimally logs certain bulk operations (e.g., bulk import, index rebuild).
- Supports full, differential, and transaction log (incremental) backups.
Does IDrive® 360 support backup or restore of SQL databases with unicode characters in the database name?
No. IDrive 360 does not support backup or restore of SQL databases whose database names contain Unicode characters.
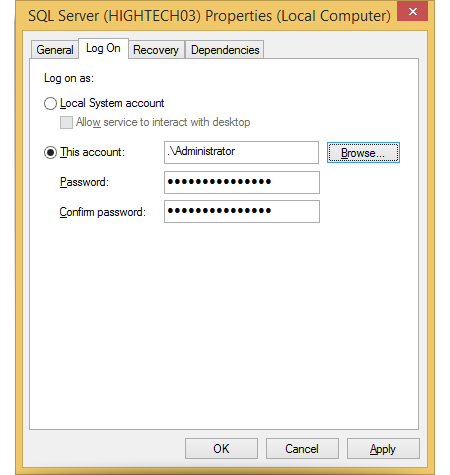
How do I run the MS SQL Server instance using an administrator or local account?
To configure the SQL Server instance to run under an administrator or local account:
- Open the ‘Services’ console (services.msc).
- Locate and right-click the ‘SQL Server (InstanceName)’ service, then select ‘Properties’.
- Go to 'Log On' and select 'This account'.
- Browse the administrator account, enter the account credentials, and click 'Apply'.
- Restart the SQL Server service.
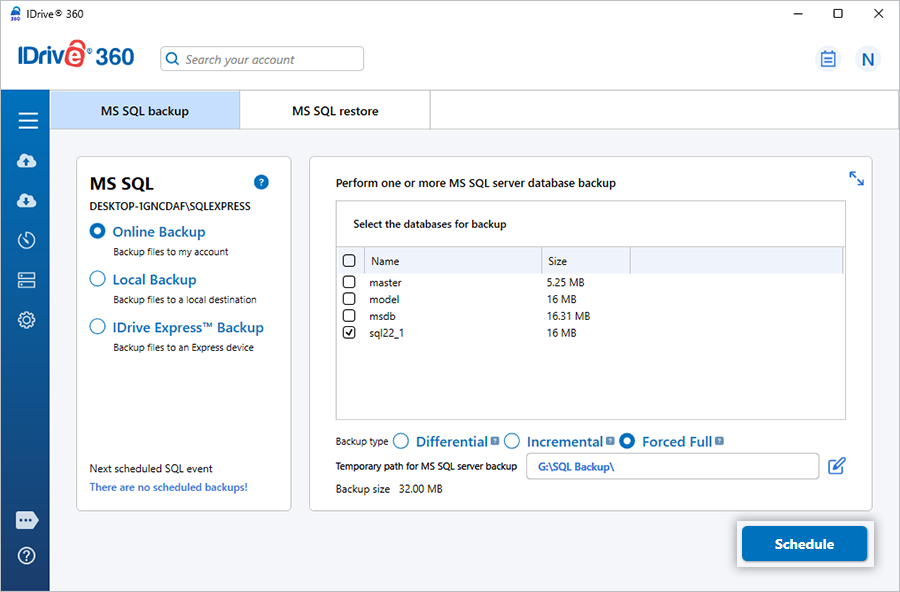
How can I back up an MS SQL Server database to a NAS or mapped network drive?
To perform a database backup to a NAS or mapped network location, first ensure that the network path is mapped to your system.
To back up the database,
- Click 'Server Backup'. The slider menu appears.
- Click 'MS SQL'. The MS SQL connection screen appears with 'MS SQL backup' selected by default.

- Provide the required MS SQL Server authentication details and click 'Connect to MS SQL'.

- Select 'Online Backup', 'Local Backup' or 'IDrive® 360 Express™ Backup'.
- Select the databases you want to back up.
- Select backup type: 'Differential', 'Incremental', or 'Forced Full'.
- Select the mapped network drive or NAS location as the destination for the SQL backup file.
- Click 'OK', then click 'Schedule Now'.
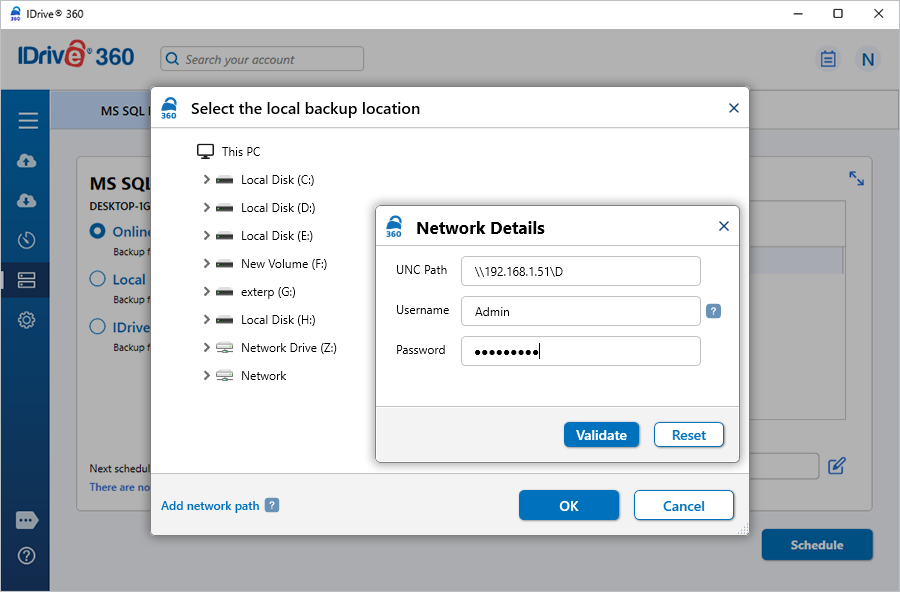
- Enter the mapped drive or NAS credentials (username and password) and click 'Authenticate'.
- In the 'Scheduler', configure the backup schedule and click 'Save Changes'.
How can I restore an MS SQL Server database backup from a NAS or mapped network drive
To restore a database from a NAS or mapped network drive, ensure that the network location is mapped to your system.
To restore,
- Click 'Server Backup'. The slider menu appears.

- Click 'MS SQL'. The MS SQL connection screen appears.
- Click 'MS SQL restore'.
- Provide the required MS SQL Server authentication details and click 'Connect to MS SQL'.
- Browse to the ‘IDSQLBackup’ folder on the mapped network drive or NAS location and select the SQL database backup file.
If required, download the ‘IDSQLBackup’ folder from your IDrive 360 account or local drive to the mapped location before proceeding. - Click ‘OK’.

- Select the database(s) to restore.
- Click 'Restore Now'.
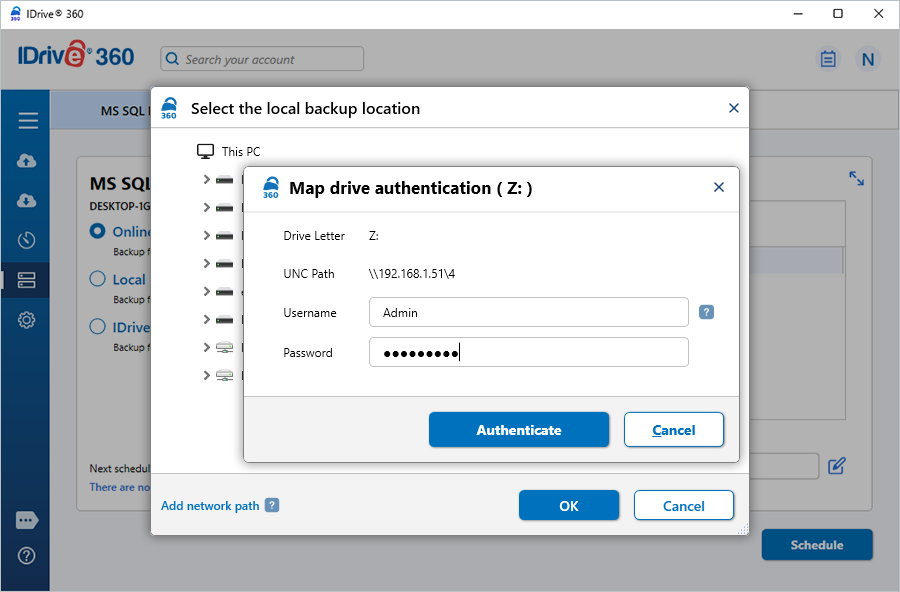
- When prompted for network authentication, enter the username and password for the NAS/mapped drive and click ‘Authenticate’.
Note: It is recommended to run the SQL Server instance service using an administrator or local system account to ensure proper access to NAS or mapped network drives during the restore process.
How do I change the database recovery model from Simple to Full or Bulk-logged to enable incremental backup?
To enable incremental (transaction log) backups, you must change the SQL Server database recovery model from Simple to Full or Bulk-Logged.
To change the recovery model,
- Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and log in.
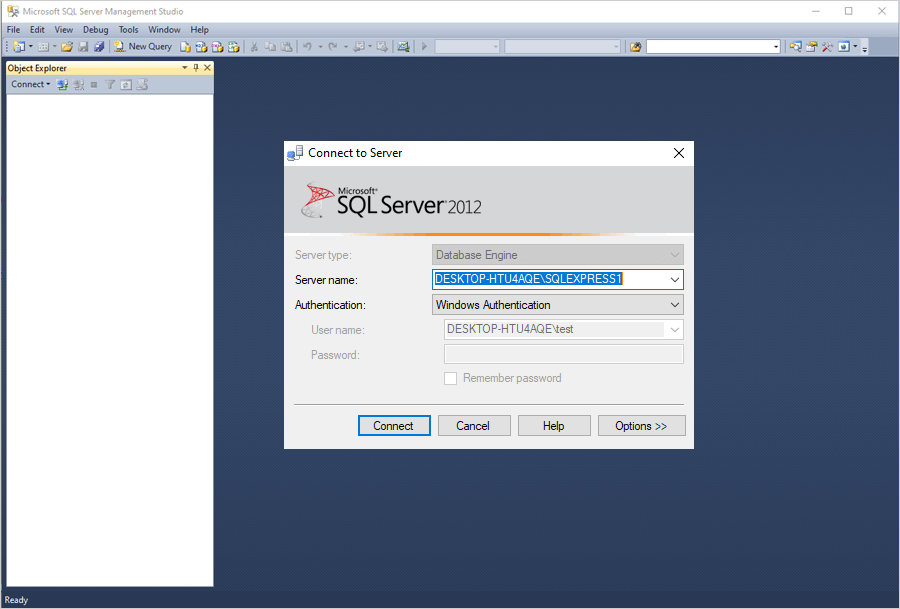
- In ‘Object Explorer’, expand the ‘Databases’ folder.
A list of databases will appear. - Right-click the required database and select 'Properties'.
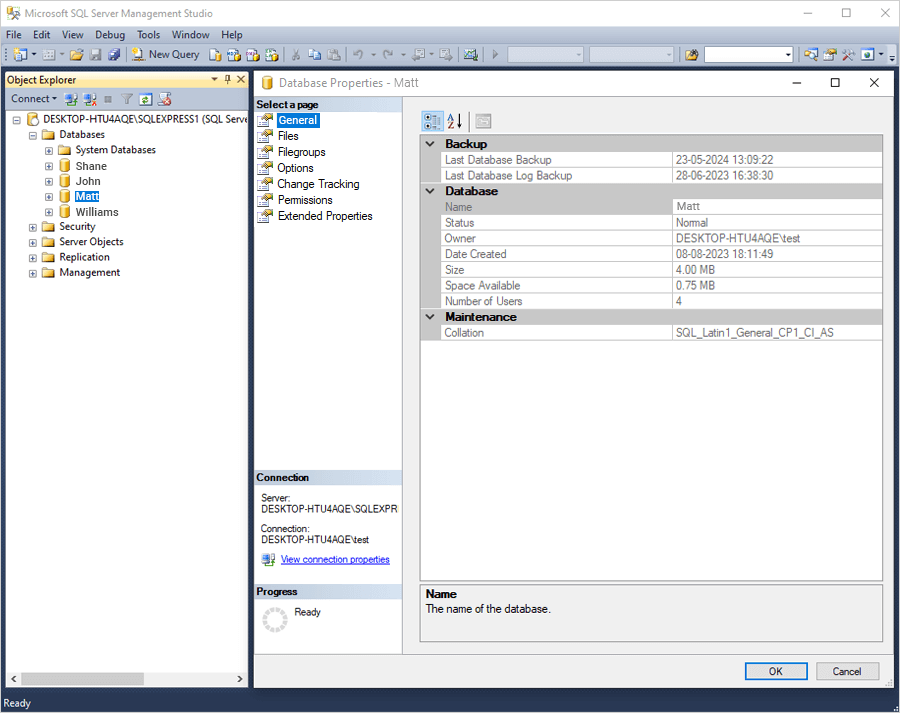
- In the ‘Database properties’ window, select 'Options'.
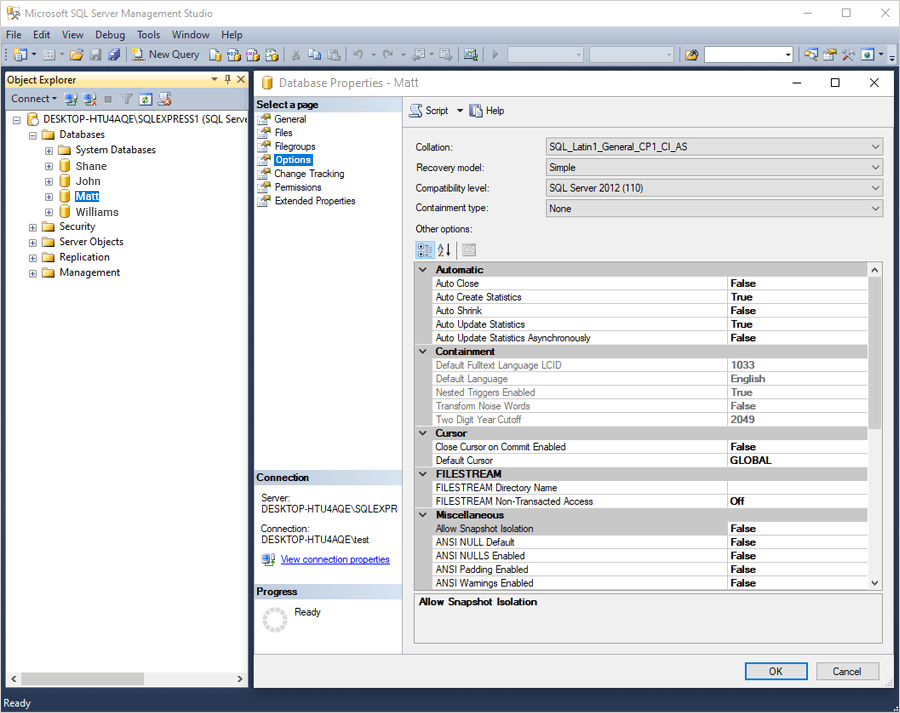
- Under ‘Recovery model’, select Full or Bulk-logged from the dropdown.
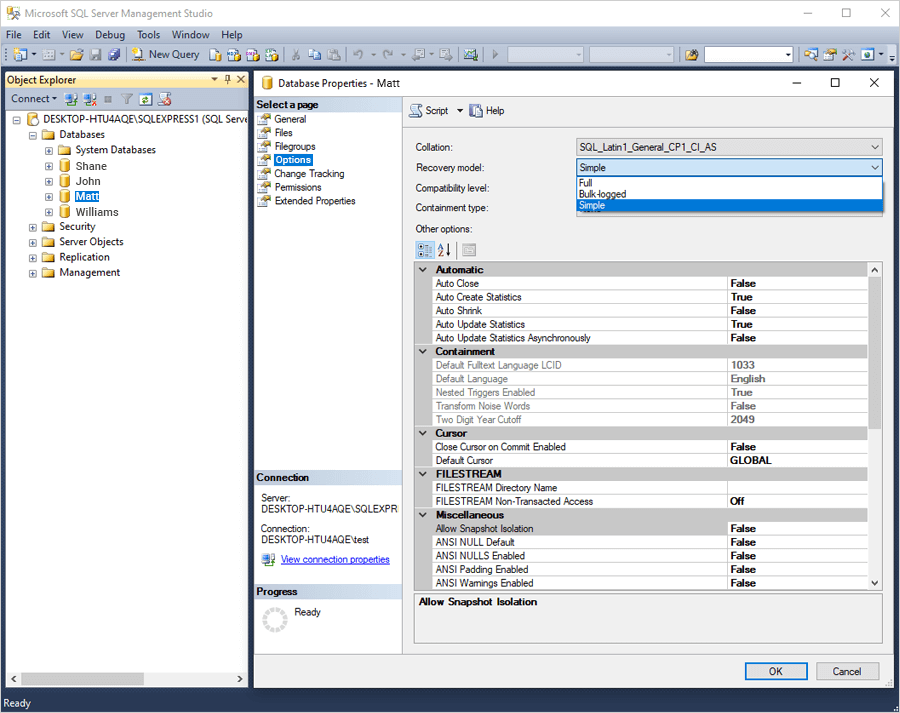
- Click 'OK'.
Once the recovery model is updated, you can use the Incremental Backup option in the IDrive 360 desktop application to back up transaction log changes.
How to remove unwanted MS SQL Server databases from the restore list?
To remove databases that are not required for restore,
- Sign in to the IDrive® 360 desktop application and click 'Server Backup'. The slider menu appears.
- Click 'MS SQL' to open the MS SQL connection screen.
- Click 'MS SQL restore'.
- Provide the required MS SQL Server authentication details.
- Click 'Connect to MS SQL'.
- Browse and select the ‘IDSQLBackup’ file that was restored earlier from your IDrive 360 account or local drive.
After the ‘IDSQLBackup’ file loads, the ‘SQL Server Backup/Restore wizard’ appears. - In the wizard, right-click the database you want to remove and select ‘Delete’.
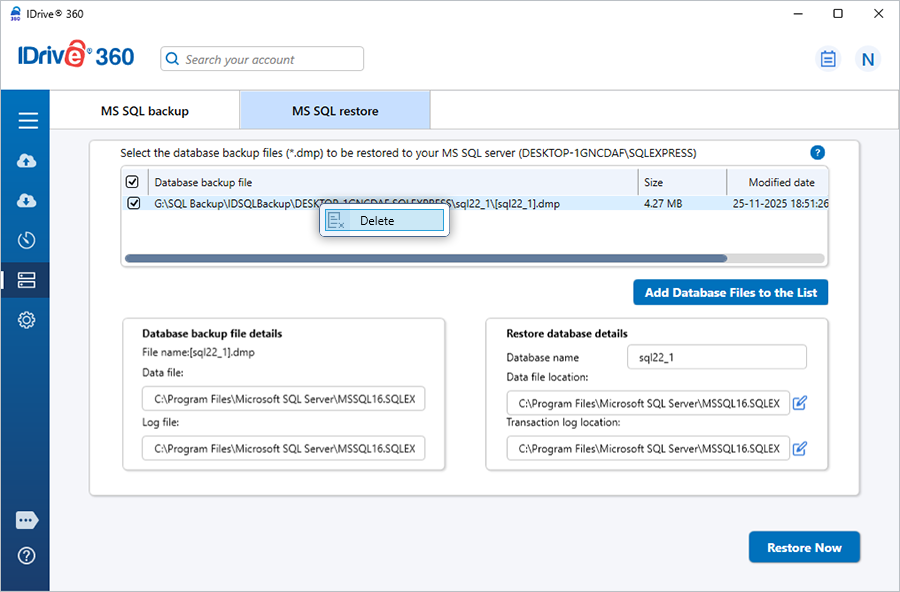
- In the confirmation prompt, click 'Yes'.